Short History of Byzantine Empire and its Capital Constantinople
- Alternate History Byzantine Empire Wiki
- The Byzantine Empire And Russia
- Alternate History Byzantine Empire
- Alternate History Byzantine Empire Definition
- How Long Byzantine Empire Last
A new mini serie in english which will last 2 or 3 episodesI don't own the musics like the picture from deviant art that I used they go to their rightfull o.
- Works inspired by Roman history, or by works of fiction and non-fiction about Rome Science fiction. Empire of the Atom, by A. Van Vogt, translates Graves' novel about Claudius(above) into a science fiction context.; The Foundation series by Isaac Asimov, about the fall of a galactic empire, is derived from Gibbon's Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire.
- Greek and Latin languages were part of the repertoire of the educated in Constantinople, the capital that Emperor Constantine developed in the East.
- About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
At the beginning of the 4th century, the Roman Empire was tired of fighting the barbarians in the West and the Sassanids (Persians) in the East. These developments caused the eternal capital Rome to lose its importance. Emperors, who wanted to be close to critical regions both in the West and East, were in search of another capital instead of Rome.
Diocletian was the first emperor to move the center of the empire to the East. He lived in Nicomedia in the early years of his reign. However, it was Constantine, who was known as the Great, who would permanently change the capital.
The Foundation Of Constantinople
Roman Empire had vast borders when Constantine managed to be the sole ruler of Rome. He wanted to create a new city in the east. For this purpose, he chose Byzantium, a small Greek city. Romans reconstructed and adorned the city and named it “New Rome” (330 AD) which eventually became the famous Constantinople.
It was not an arbitrary decision for Emperor Constantine to establish such a city. This decision was based on political and economic reasons. The fact that Istanbul was surrounded by the sea on three sides made it impossible for the barbarians to take over the city. At the same time, it was a great advantage to be close to the Eastern Mediterranean, the center of trade at that time.
Constantine built the Great Palace, Hippodrome and Forum of Constantine in the new city, where he lived until his death. When he died, he was buried in Church of the Holy Apostles.
The Division of the Roman Empire as East and West
After Constantine’s death, the empire began to decline. Theodosius I ascended the throne when the Roman Empire was in great danger. Theodosius showed a very successful administration and secured the borders. But he died unexpectedly in his 40s.
After the death of Theodosius, the empire was divided into east and west. One of Theodosius’ sons, 12-year-old Honorius, became the Western Roman Emperor, while his 18-year-old son, Arcadius, became the head of Eastern Rome.
However, after a while most of Western Europe (formerly the heartland of the empire) fell to barbarian invaders (476 AD). According to some historians, Emperor Constantine predicted this disaster. This was the main reason why he moved the capital to the East 150 years before the fall of Rome.
Alternate History Byzantine Empire Wiki
Western and Eastern Roman Empires in 395 AD
Why Eastern Roman Empire is called Byzantine?
The conquest of Rome by the barbarians brought the end of Western Roman Empire. however, the Eastern Roman Empire survived for a thousand years until 1453, the year of the fall of Constantinople.
The Eastern Roman Empire was renamed by the historians in the modern age as the Byzantine Empire. The reason for this was that the Greek-speaking eastern half of the empire developed a different culture as time went on.
The Pagan Roman Empire of ancient times and the Christian Byzantine Empire of the Middle Ages were quite different. No matter how much Byzantine Empire was still on the military, administrative and legal basis established by the Roman Empire, another culture had emerged. Historians derived this new name from the Byzantium, the Greek name of the city of Constantinople.
History of Byzantine Empire and Constantinople
Rise of Byzantine Empire under Justinian’s Rule
Emperor Justinian became the greatest emperor who ruled the Byzantine Empire. Justinian, a great statesman, was known for his hard work. Under Justinian, great conquests were made and magnificent structures were built. The generals Belisarius, Mundus and Narses conquered in the name of Justinian.
Justinian’s greatest goal was to take back Rome, the eternal capital of the empire. Without the Italian peninsula, it was impossible to claim rights over the Roman Empire‘s legacy. Justinian, expanded the Eastern Roman Empire’s borders into Middle East, Northern Africa and Western Europe.
Today Justinian is known for Constantinople’s greatest building, Hagia Sophia. Finished in 537, it reigned as the largest and greatest church of Christendom for a thousand years.
Justinian is also famous for creating Codex Justinianus, which is the codification of Roman law. He left a vast but ready-to-collapse empire to his successors.
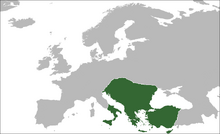
Byzantine Empire Map
Byzantine Empire Under Attack
After the death of Justinian, Arabs, Slavs and Turks attacked the Byzantine borders. Emperor Heraclius managed to secure borders temporarily, but it did not last long. In a short time, many important cities such as Antioch, Jerusalem and Alexandria were lost.
In the 11th century, the Seljuk Turks migrated from Central Asia and built a powerful empire in Persia. The Turks, having a strong land army, posed a great danger to the eastern borders of Byzantium. A war between the Seljuk Turks and the Byzantines had become inevitable.
The Byzantine Empire And Russia
The Seljuks won a great victory in the Battle of Manzikert and swiftly advanced into Anatolia. The fact that Muslim forces were so close to Europe triggered the Pope to take urgent measures.
Byzantine Empire and Seljuk Turks
Sack of Constantinople by Crusaders
Following the Pope’s order, the Crusader armies of Europe marched through Constantinople in the 12th and 13th centuries. They battled with the Seljuk Turks and overran them. Byzantines took back majority of the Anatolia from Turks until they lost it to another Turkish kingdom: Seljuk Sultanate of Rum.
The crusaders continued to attack the East for several centuries. However, when it came to the Fourth Crusade, they attacked Constantinople, the heart of Orthodox Christianity. Latin invasion lasted from 1204 to 1261 and it was finally repelled by a Byzantine prince.
Yet, the Byzantines and the Eastern Church never forgot these terrible events. Some even claimed “Better Turkish turban than Latin Miter” before the fall of Constantinople.
It should be emphasized that the Eastern and Western Churches have never been able to establish healthy communication for centuries. it was only in the 1950s that the leaders of the two churches came together.
Latin Armies in Constantinople
Fall of Constantinople and The Byzantine Empire
By the late 13th century, Byzantine Empire’s power was much reduced in Anatolia. The Byzantine army had never really recovered and strengthened after Latin invasion. Turkish warlords on its eastern borders around Nicaea became serious threats.
One of these Turkish principalities, established by a chieftain named Osman Ghazi (aka Othman), grew into the Ottoman Empire. Ottoman Turks conquered the imperial capital of Constantinople in 1453 and proclaimed it their capital. Constantinople once again became the capital of a rising empire.
Byzantine Empire History Tour in Istanbul
Alternate History Byzantine Empire

Alternate History Byzantine Empire Definition
If you are interested to see the Byzantine heritage in Istanbul, consider joining the history tours by Serhat Engul. Please check Private Tour of Byzantine Istanbul website for more information.