- Draw and view structures in 2D, or render in 3D to view from any angle
- Draw Markush structures, structures with delocalization, and polymers
- Choose from a wide range of special bond types including aromatic, delocalized, undefined single and double stereo, quadruple, and coordination bonds
- Automatically assign hydrogen atoms and charges to fill valence
- View all the suggested tautomeric forms for your structure
- Generate structures from InChI and SMILES strings
- Search for structures in the built-in dictionary of over 170,000 systematic, trivial, and trade names
- Search for chemical structures in various file formats throughout your computer’s file systems. (SK2; MOL; SDF; SKC; CHM; CDX; RXN; Adobe PDF; Microsoft Office DOC, XLS, PPT; and ACD/Labs databases CFD)
Operating System Requirements:
- Microsoft Windows 8.1 (x64)
- Microsoft Windows 10 (x64)
Chemsketch For Mac
Hardware Requirements

Chemsketch free download, and many more programs. Chemsketch free download, and many more programs.
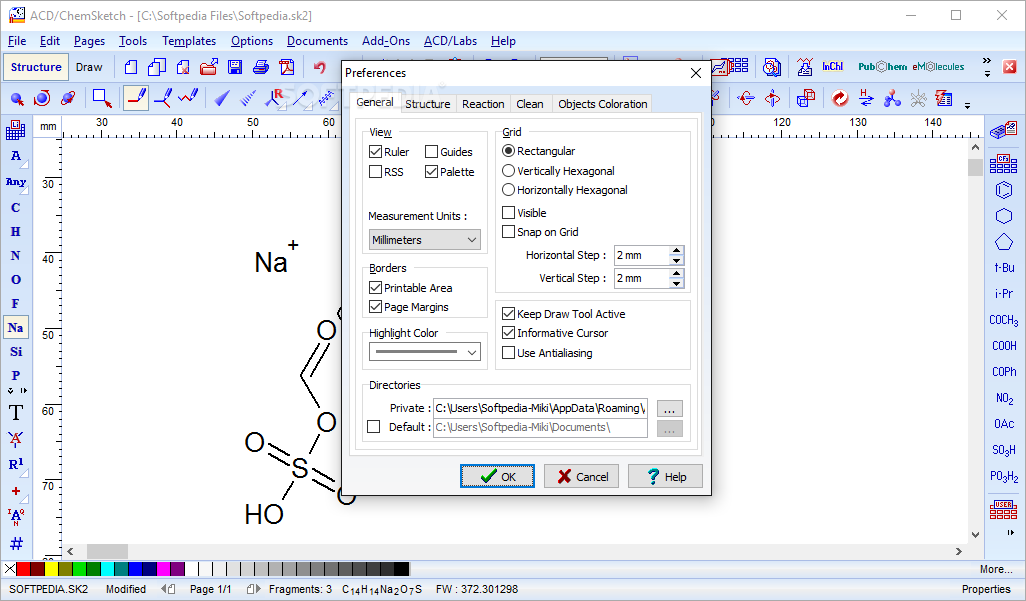
- ACD/LABS™ SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT. GRANT OF LICENSE. Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc. ('ACD/Labs') grants ('Licensee'), a non-exclusive, non-transferable license during the term of this license agreement (the 'Agreement') to use and display the computer program titled Freeware ACD/ChemSketch (the 'Software') contained herewith solely for its own internal purposes and for non.
- ACD/ChemSketch is a molecular modeling program used to create and modify images of chemical structures.Also, there is a software that allows molecules and molecular models displayed in two and three dimensions, to understand the structure of chemical bonds and the nature of the functional groups.
Chemical Structure Search

Chemsketch Free

- Microsoft Windows compatible PC with minimum 2-core CPU
- 4 GB or more RAM
- Minimum of 40 GB of disk space
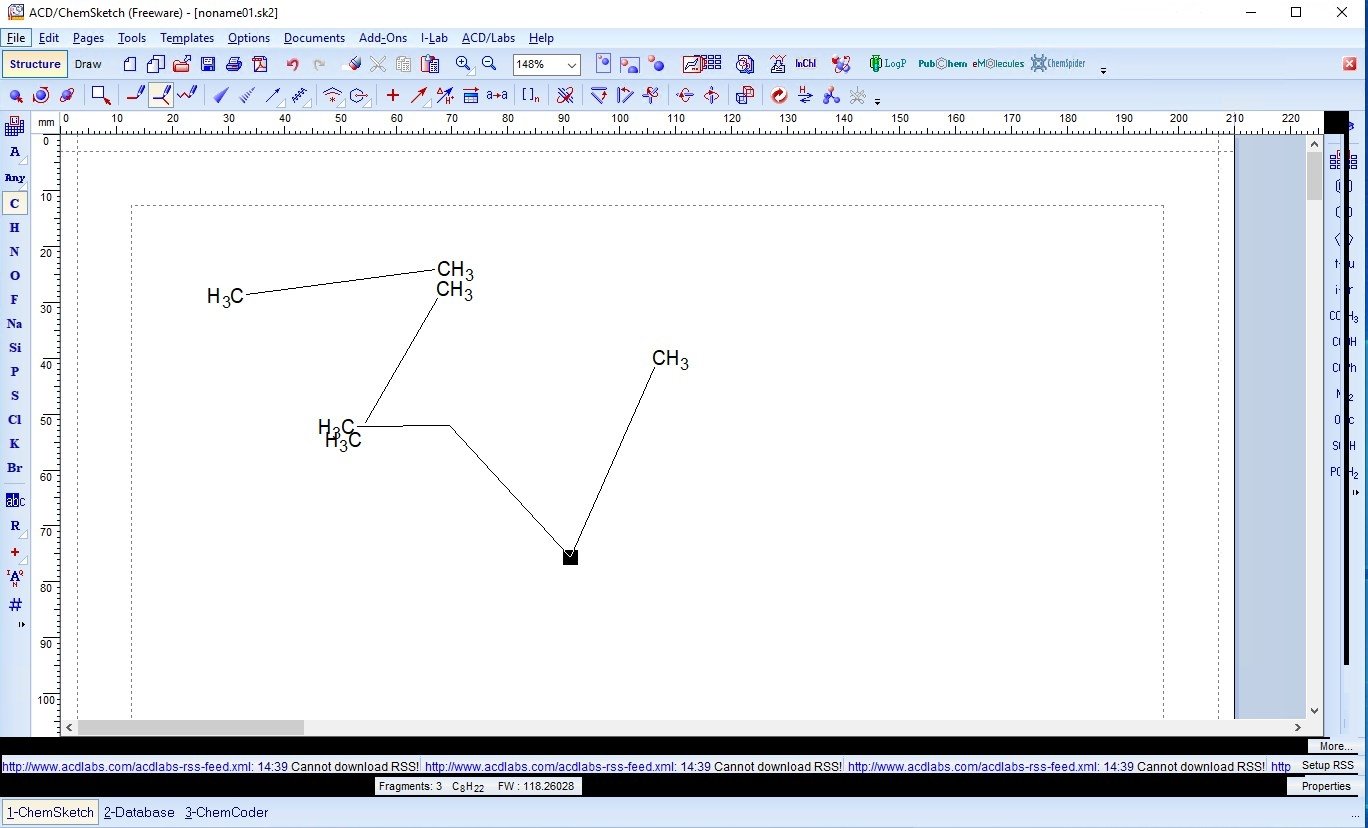
Drawing Structures with ChemSketch It is amazing that ChemSketch is freeware because it is a quite powerful chemical structure drawing program. One of its few drawbacks is that it is somewhat complicated to learn. However, if you have any experience with drawing programs then some aspects of it should be easier for you to learn. Introduction
Modes
Tools
Tools | Structure Propertiesin Structure mode The Structure Properties panel is open. The panel can be moved anywhere, on or off the main window. The two most commonly used tabs are 'Common' and 'Atom'. Tools | Panels in Drawing Mode The panels that are open in the Draw Mode pertain mostly to text formatting (Font, Pen, Paragraph) and drawing (Arrow, Fill). I.Chemical Structures
II. Drawing Tools and Objects
III.Templates
IV. Extra Features
V. Saving Files as Images
VI.Embedding ChemSketch drawings in Windows applications
ChemSketch Practice 1. Reproduce the structures shown in the Practice pages linked below. Drawing each of the practice structures will help you learn some of the features of ChemSketch, e.g. drawing rings from the template menu, changing atom symbols, drawing carbon chains, etc. If you need to know how to do something, open Help. 2. Many times you will have to expand a collapsed structural formula and show the correct sterochemistry and geometry. This would be a good time to review hybridization, geometry, bondangles,non-bondingelectrons, formalcharges, etc. Here are a few examples, with answers.
3. Read the OLE and OLE Limitations documents mentioned above, after they have been assigned in class. Select a ChemSketch object in the ChemSketch window. Copy it. Embed it into a Word page using Paste and then Paste Special.... Double-click the object. Is there any difference between the two methods? Can you Link the ChemSketch object? Choose Insert | Object in Word. Choose Create New ACD ChemSketch object. Draw an object and finish embedding in Word. What do you do if you choose Create From File? Can you Link the file? 4. Insert an equation into a ChemSketch document using Equation Editor. 5. Can you embed a Word document inside a ChemSketch document? An Excel spreadsheet? If you can embed these objects, and you want to edit them, do you need to be in the Structure or Draw modes, or either? SMILES Structure Notation Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry Specification SMILES is widely used as a general-purpose chemical nomenclature and data exchange format. The 'character string' (the sequence of ASCII characters) represents a structrual model of a molecule. The string can be read by both humans and computers -- computers cannot typically read the two- and three-dimensional structures generated by chemists. AtomsAn individual element is represented by a standard atomic symbol. It is required to be present for each atom, except Hydrogen. Elements and charged species are written within brackets. examples: [B] element boron Elements in the following 'organic subset' typically have well-defined valences and may be written without brackets if the number of attached hydrogens conforms to the lowest normal valence consistent with explicit bonds. This subset, and their lowest normal valences, are: examples: BondsSingle, double and triple bonds are represented by the symbols `-', `=' and `#', respectively. Alternatively, sp2-hybridized atoms may be represented in lower case. Single bonds may be omitted. If an atom is enclosed in brackets, all explicit Hydrogens must be shown, as in the last example for ethane, below. examples: CC ethane CC#C propyne BranchesBranches are specified by enclosing them in parentheses, and can be nested or stacked. The connection to a parenthesized branch is to the left. CC(C)C(=O)OC methyl isobutyrate CCN(CC)CC triethylamine Ringsexamples: C1CCCC1 cyclopentane CC1CCC1 methylcyclobutane c1ccccc1 benzene Geometric Isomerismexamples: F/C=C/F trans-1,2-difluoroethene FC=C/F cis-1,2-difluoroethene SSMILES is an extremely simplified subset of SMILES used for expressing 'normal' organic chemicals, i.e., neutral molecules with atoms at their normal organic valences. There is no need for brackets, charges, aromatic specifications, etc. In fact the rules for the language are basically:
Which is pretty much what you see above. Practice with easy structures by drawing them in ChemSketch and then generating the SMILES notation. Here are a few examples. ChemSketch 3D ChemSketch is not only a molecular drawing program, it is also a molecular visualization program. You can toggle back and forth between the two programs. I. To switch to the 3D window from the ChemSketch window:
II.3D Display
III.Measurements
IV. Saving Files as Images
Answers 1. Use the continuous chain tool and the 'C' atom button to draw a zig-zag with 4 carbons. Then choose Tools | Add Explicit Hydrogens to sprout hydrogens at each of the carbons (or on selected carbons). Use the stereobond tools. Use the 'Lasso' tool to move the C's and H's around so they look like they are in the front and back of the zig-zag. All the carbons are sp3-hybridized, tetrahedral geometry, ~109 deg. bond angles. 2. Draw acetaldehyde. Make stereobonds. Add non-bonding electrons (Template | Organizer | Reactionsymbols). Press ^G to group the electrons with the molecule. Add orbitals (Template | Organizer | Orbitals). In Draw mode, use text tool to add C and O atom labels and use the line tool to add bonds. Group all segments. The carbonyl carbon is sp2-hybridized, trigonal planar geometry, ~120 deg. bond angles. The methyl carbon is sp3-hybridized, tetrahedral geometry, ~109 deg. bond angles. 3. Notice particularly the effect of the non-bonding pair of electrons on the geometry of the sulfur dioxide molecule (compare with linear CO2; the carbon is sp-hybridized, linear geometry, 180 deg. bond angle). What geometry is exhibited by PCl5?Review VSEPR theory for atoms with 5 or 6 single bonds. |