
- See More Results
- Afp Vs Smb Vs Nfs Performance
- SMB Vs AFP For NAS Using Only Macs
- I'm Writing This Comment In 2016, Apple Defaults Now To SMB, However MacOs Performance Remains Abysmal In SMB. On Gigabit Ethernet, It's Generally...
We setup some shares on the FS1018 from Synology to see which one is faster. Thanks to 'Music: Little Idea - Bensound.com' Thanks for watching!
- Question: Q: AFP vs SMB Performance. The problem is that you cannot edit Microsoft Office files (.dotx,.xlsx, etc) from an NFS share on Mac. When you open the.
- The side-by-side comparison of the Asustor AS6202T and Asustor AS6102T NAS devices’ specifications. The comparison table makes it easier to choose between the Asustor AS6202T and Asustor AS6102T.
- High Sierra: AFP vs Samba vs NFS I'm switching from an all Windows environment to OS X and a Linux server (file, mail, and Emby server). I've run Linux servers in the past and OS X a whopping 14 years ago when I had a Powerbook 17'.
Known Issues
There are currently no known problems that require additional documentation.
Release Notes
After upgrading from macOS 10.12 Sierra or lower, a client might not correctly read files from NFSv4 servers created with previous versions of macOS, OS X, or Mac OS X: If you have used older versions of the operating system to write Macintosh files to an NFSv4 server, and the server implementation supports named attributes, and the files are using Extended Attributes or forks, these attributes and forks will become temporarily inaccessible after upgrading to macOS 11.0 Big Sur.
Workaround: This is a documented policy change in Apple’s NFSv4 client as of macOS 10.13. If you like to continue using named attributes over NFSv4, you will have to enable a new NFSv4 mount option on each client. This option is called Enforce extended attributes and named forks if supported by server in NFS Manager. For Apple’s documentation, enter the command man 5 nfs in Terminal.
If you add automount triggers to the Finder sidebar, the Finder may intermittently remove them: In case your system is configured to use NFS automounts, a user may drag the topmost folder of the automounted file system or an object from that hierarchy into the Favorites section of the sidebar of a Finder window. This way, the automount can be triggered easily, without needing an additional alias object on the Desktop. The Finder might unexpectently lose such sidebar entries, however.
Workaround: This is a known issue of the Finder. We hope that Apple will resolve this problem in future versions of macOS. A possible alternative is to create an alias for the automounted folder (by using either the Finder or the feature Create Desktop icon of NFS Manager) and to drag the alias to the sidebar.

Some applications cannot process files on an NFS server if those files have not been created using the identical file service protocol: If you write a Macintosh file with Extended Attributes or forks to an NFS server using a different protocol (like AFP, or SMB, or a different NFS standard like NFSv3 vs. NFSv4, or by creating this file directly on the server writing it to the local hard disk), you may later have problems opening this file. Each file sharing protocol uses different techniques to handle Extended Attributes. Those techniques are not compatible with each other, so you cannot write a file with attributes using one protocol but read it with another protocol.
Workaround: You should avoid using different file server protocols at the same time when reading and writing Macintosh files with Extended Attributes. Even when you only use NFS, you must take care either not to allow simultaneous access via NFS3 and NFSv4, or to enforce matching options for the use of named attributes on all clients.
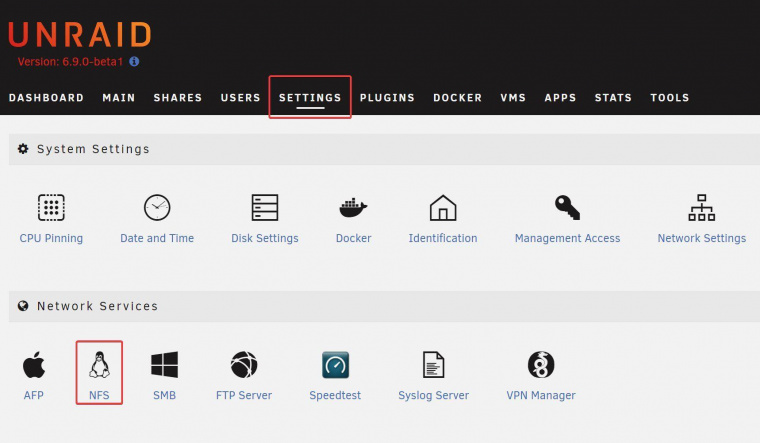
Go to 'Control Panel' > 'Network Services' > 'Win/Mac/NFS' to configure networking services.
Microsoft Networking
To allow access to the NAS on Microsoft Windows Network, enable file service for Microsoft networking. Specify also how the users will be authenticated.
Standalone Server
Use local users for authentication. The NAS will use the local user accounts information (created in 'Privilege Settings' > 'Users') to authenticate the users who access the NAS.
| • | Server Description (optional): Describe the NAS so that the users can easily identify the server on Microsoft Network. |
| • | Workgroup: Specify the workgroup to which the NAS belongs. A workgroup name supports up to 15 characters but cannot contain: ' + = / : | * ? < > ; [ ] % , ` |
AD Domain Member
Use Microsoft Active Directory (AD) to authenticate the users. To use this option, enable Active Directory authentication in 'Privilege Settings' > 'Domain Security' and join the NAS to an Active Directory.
LDAP Domain Authentication
Use Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory to authenticate the users. To use this option, enable LDAP authentication and specify the settings in 'Privilege Settings' > 'Domain Security'. When this option is enabled, you need to select either the local NAS users or the LDAP users can access the NAS via Microsoft Networking.
Advanced Options
| • | WINS server: If the local network has a WINS server installed, specify the IP address. The NAS will automatically register its name and IP address with WINS service. If you have a WINS server on your network and want to use this server, enter the WINS server IP. Do not turn on this option if you are not sure about the settings. |
| • | Local Domain Master: A Domain Master Browser is responsible for collecting and recording resources and services available for each PC on the network or a workgroup of Windows. When you find the waiting time for connecting to the Network Neighborhood/My Network Places too long, it may be caused by failure of an existing master browser or a missing master browser on the network. If there is no master browser on your network, select the option 'Domain Master' to configure the NAS as the master browser. Do not turn on this option if you are not sure about the settings. |
| • | Allow only NTLMv2 authentication: NTLMv2 stands for NT LAN Manager version 2. When this option is turned on, login to the shared folders by Microsoft Networking will be allowed only with NTLMv2 authentication. If the option is turned off, NTLM (NT LAN Manager) will be used by default and NTLMv2 can be negotiated by the client. The default setting is disabled. |
| • | Name resolution priority: You can select to use DNS server or WINS server to resolve client host names from IP addresses. When you set up your NAS to use a WINS server or to be a WINS server, you can choose to use DNS or WINS first for name resolution. When WINS is enabled, the default setting is 'Try WINS then DNS'. Otherwise, DNS will be used for name resolution by default. |

| • | Login style: DOMAINUSERNAME instead of DOMAIN+USERNAME for FTP, AFP, and File Station: In an Active Directory environment, the default login formats for the domain users are: |
| o | FTP: domain+username |
See More Results
| o | AFP: domain+username |
When you turn on this option, the users can use the same login name format (domainusername) to connect to the NAS via AFP, FTP, and File Station.
| • | Automatically register in DNS: When this option is turned on and the NAS is joined to an Active Directory, the NAS will register itself automatically in the domain DNS server. This will create a DNS host entry for the NAS in the DNS server. If the NAS IP is changed, the NAS will automatically update the new IP in the DNS server. |
| • | Enable trusted domains: Select this option to load the users from trusted Active Directory domains and specify their access permissions to the NAS in 'Privilege Settings' > 'Shared Folders'. (The domain trusts are set up in Active Directory only, not on the NAS.) |
| • | Enable Asynchronous I/O: Enable this option to speed up the SAMBA performance, but an UPS is strongly recommended to prevent power interruption if this option is to be enabled. |
| • | Highest SMB version: Choose the version of the SMB protocol (Server Message Block) from the drop down list for your Microsoft Networking operations. If you are not sure, please use the default one on the list. |
Apple Networking
To connect to the NAS from Mac, enable Apple Filing Protocol. If the AppleTalk network uses extended networks and is assigned with multiple zones, assign a zone name to the NAS. Enter an asterisk (*) to use the default setting. This setting is disabled by default. To allow access to the NAS from Mac OS X 10.7 Lion, enable 'DHX2 authentication support'. Click 'Apply' to save the settings. You can use the Finder to connect to a shared folder from Mac. Go to 'Go' > 'Connect to Server', or simply use the default keyboard shortcut 'Command+k'. Enter the connection information in the 'Server Address' field, such as 'afp://YOUR_NAS_IP_OR_HOSTNAME'. Here are some examples:
| • | afp://NAS-559 |
Afp Vs Smb Vs Nfs Performance
Note: Mac OS X supports both Apple Filing Protocol and Microsoft Networking. To connect to the NAS via Apple Filing Protocol, the server address should start with 'afp://'. To connect to the NAS via Microsoft Networking, please use 'smb://'. |
NFS Service
To connect to the NAS from Linux, enable NFS service. To configure the NFS access right to the shared folders on the NAS, go to 'Privilege Settings' > 'Share Folders'. Click the Access Permission button on the 'Action' column.Select NFS host access from the drop-down menu on top of the page and specify the access right. If you select 'No limit' or 'Read only', you can specify the IP address or domains that are allowed to connect to the folder by NFS.
| • | No limit: Allow users to create, read, write, and delete files or folders in the shared folder and any subdirectories. |
| • | Read only: Allow users to read files in the shared folder and any subdirectories but they are not allowed to write, create, or delete any files. |
| • | Deny access: Deny all access to the shared folder. |
SMB Vs AFP For NAS Using Only Macs
Connecting to the NAS by NFS

On Linux, run the following command:
mount -t nfs <NAS IP>:/<Shared Folder Name> <Directory to Mount>
For example, if the IP address of your NAS is 192.168.0.1 and you want to link the shared folder 'public' under the /mnt/pub directory, use the following command:
mount -t nfs 192.168.0.1:/public /mnt/pub
Note: You must login as the 'root' user to initiate the above command. |
I'm Writing This Comment In 2016, Apple Defaults Now To SMB, However MacOs Performance Remains Abysmal In SMB. On Gigabit Ethernet, It's Generally...
Login as the user ID you define, you can use the mounted directory to connect to your shared files.
url http://www.yourdomain.com/help/index.html?win_mac_nfs.htm
© 2015 QNAP Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. |